Wiring harnesses, crucial for transmitting electrical signals and power, demand high-quality materials and adherence to safety standards. At Cloom, we recognize this, ensuring top-tier products through a meticulously designed manufacturing process.
Understanding Wiring Harness Production
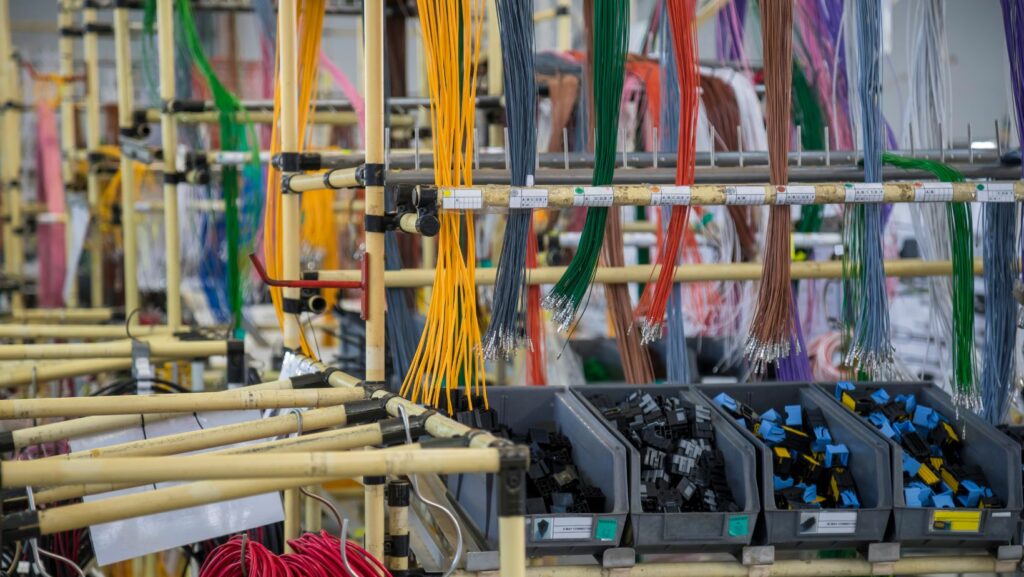
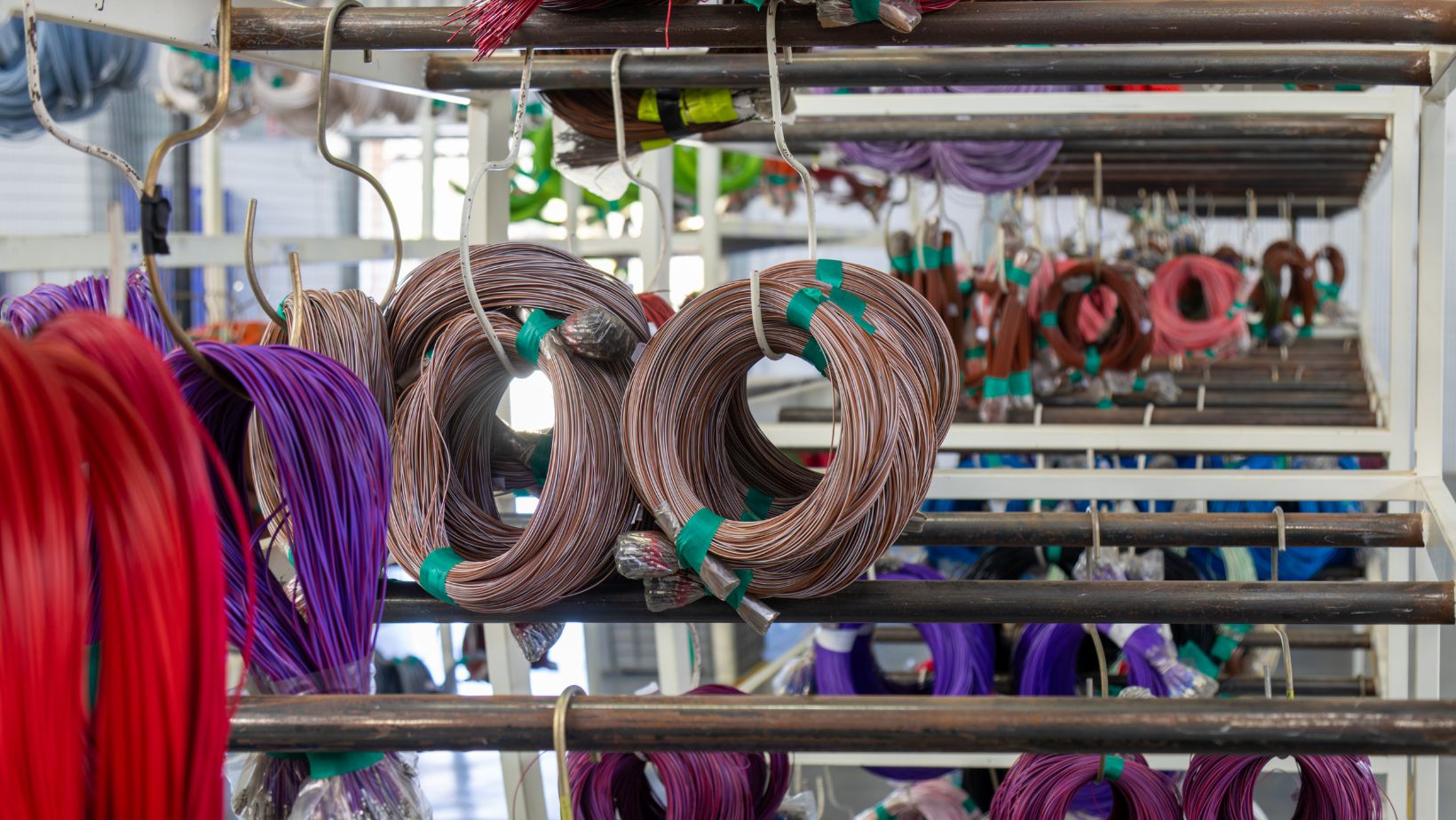
A custom wiring harness, or cable assembly, is formed when cables, wires, and connectors are combined into an intricate structure for power and signal transmission. Wire harness manufacturers specialize in assembling these components, employing various techniques like crimping, soldering, stripping, and wire joining.
Each harness is tailored to a specific application, utilizing numerous wires and connectors. Complexity varies depending on the intended use. These harnesses are prevalent in industries like industrial, aerospace, and automotive.
What Your Contract Manufacturer (CM) Needs
To produce a harness that perfectly suits the application, the CM requires precise information, including:
- Wire lists detailing colors, nets, and connectors.
- Comprehensive connector data with images showing pin locations.
- A Bill of Materials (BOM) with part numbers.
- Assembly drawings with instructions, label placements, and tolerances.
- Final test specifications.
Wiring Harness Manufacturing Process
- Design review: The CM reviews the design and BOM for completeness, evaluating parts for cost, performance, and availability. Any issues lead to seeking replacements.
- Materials preparation: Once the BOM is approved, materials and components are procured to initiate production.
- Assembly documentation: Based on customer input, the CM prepares assembly documentation, including step-by-step instructions, illustrations, and test procedures. An assembly panel with pegs at specified points is also prepared.
- Prototyping: A working model is created and tested for its intended application. It undergoes thorough inspection and comparison with CAD models to ensure all drawing specifications are met. Failure necessitates project rework.
- Inbound inspection: Wires, cables, and other components from suppliers are inspected and tested before assembly using a digital system to track data on wire gauges, connector damage, spacing, etc.
- Assembly: After prototype approval, assembly begins, with quality checks and inspections throughout to ensure high-quality final products. Precision at this stage saves time, enhances reputation, and prevents losses.
- Wire stripping, crimping, and termination: Insulation is removed, exposing the metal conductor. Careful handling prevents damage and safety risks. Crimping connects wires to terminals, requiring precision to avoid signal disruption or wire damage. Finally, terminal pins are attached through soldering or insertion. Microscopes may be used for accuracy on tiny assembly boards.
- Testing: The harness is tested for functionality, including continuity, pull, and megohm tests, along with visual inspections. Adjustments are made if needed.
Manufacturing Challenges
Manual assembly often surpasses machines due to intricate processes demanding human precision. Some of these include:
- Taping breakouts
- Installing cables through conduits and sleeves
- Binding wires with ties, clamps, and tape
- Installing terminated wires of varying lengths
- Multiple wire crimps
These are challenging to automate, making manual processing cost-effective. Production times can range from days to weeks, extended by design complexity.
However, automation aids in tasks like crimping, soldering, cutting, stripping, twisting, and plugging terminated wires.
Conclusion
Cloom provides wiring harnesses for general use, with customization available. We offer wire cutting, stripping, twisting, coloring, binding with zip ties or cable wraps, and labeling options using heat shrink tubing or laser-printed stickers.











